Introduction to REPEC
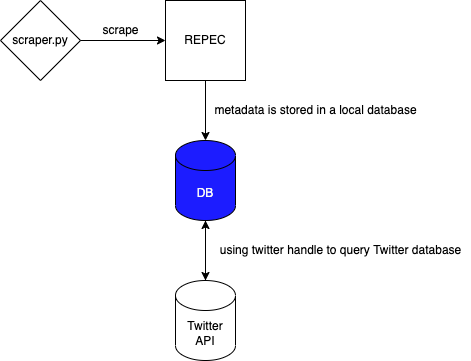
REPEC IDEAS has up to date information on 63,000 economists' publications all around the whole. It is arguably the most powerful source of information on economist activities. However, the REPEC database is difficult to navigate due to archaic formats. As such, I wrote a scraper to help scrape the website for meta data concerning the economists: journal publications, affiliations, location and paper abstracts.
This information will be especially useful in studying collaboration networks and large scale topic modeling of publications.
Methodology
The scraper I wrote will gather information on all the personal pages for economists on REPEC from this summary page. The function below returns a dataframe of all the urls of the economists.
def get_author_urls(first, last):
"""function that collects urls for authors
Parameters
----------
first : [string]
[first author name shown on page e.g. A., Baranov N.]
last : [string]
[last author name shown on page e.g. Zhou, Li ]
page in question is 'https://ideas.repec.org/i/eall.html'
Returns
-------
[pd]
[dataframe of url links for each economist]
"""
# Define target website
url = 'https://ideas.repec.org/i/eall.html'
# Setup beautiful soup
page = requests.get(url)
soup = BeautifulSoup(page.content, 'html.parser')
# Find all html links
links = soup.find_all('a', href=True)
# Filter out only useful links
url_collection = []
for i in tqdm(links,desc='Downloading links'):
author = i.text
author_url = i['href']
url_collection.append([author, author_url])
# Get rid of unnecessary links by finding the position of the first and last author
pos = [idx for idx, results in enumerate(url_collection) if (first in results[0]) or (last in results[0])]
url_collection = url_collection[min(pos):max(pos)+1]
# Some cleaning and get it into a DF
clean_urls = [reverse_comma(clean_string(u[0])).split(None, 2) + [u[1]] for u in url_collection]
cleaned = pd.DataFrame(clean_urls, columns=['first_name','middle_name','last_name','partial'])
cleaned['author_url'] = np.where(cleaned['partial'].isnull(), cleaned['last_name'], cleaned['partial'])
cleaned['last_name'] = np.where(cleaned['partial'].isnull(), cleaned['middle_name'], cleaned['last_name'])
cleaned['middle_name'] = np.where(cleaned['partial'].isnull(), None, cleaned['middle_name'])
cleaned = cleaned.drop(columns=['partial'])
return cleaned
The rest of the scraper code will then go down the list and scrape the useful information on each of the personal pages - with downtime so as not to crash the server.
One particularly useful information is the Twitter handle information on economists. This information can be used to query Twitter API for further activities of these economists. There are many academic studies that work on scientific dessemination of ideas and this could be one source of information.
Using this method, I was able to scrape the metadata for 60,000 economists into a database. I can then write SQL scripts to query for any summary statistics I would like for my research.
For the full code, please visit my github page.